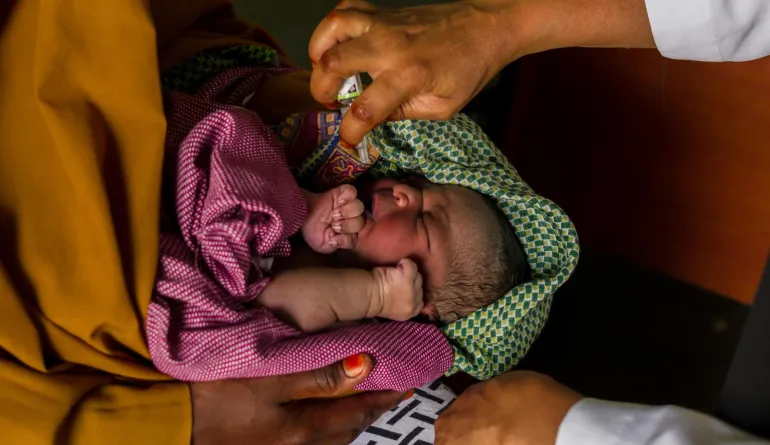
Vaccines achieved a record-breaking year in 2024, saving an estimated 1.7 million lives globally, according to Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. This marked an increase of 400,000 lives compared to 2023 and demonstrated the growing impact of vaccination programs on global health. Experts say these efforts are also generating significant economic benefits, estimated at $20 billion, through lower healthcare costs and improved productivity.
A total of 72 million children received vaccines, with major progress reported in fragile regions including Mali, Haiti, and Syria. These programs are critical in reducing preventable diseases and protecting vulnerable populations. Health authorities emphasize that routine immunization campaigns are vital for children’s survival and long-term well-being.
Significant milestones were reached in Africa, where 17 countries introduced routine malaria vaccinations for the first time. Malaria remains a major public health challenge, causing roughly 600,000 deaths each year. Experts note that these new vaccination programs have the potential to drastically reduce child mortality rates in the region.
Gavi highlighted that expanding vaccine coverage is especially important in areas affected by conflict and economic instability. Many of these regions face challenges such as limited healthcare infrastructure, poor sanitation, and high rates of infectious diseases. Vaccination campaigns in these areas not only prevent illness but also strengthen health systems by training staff, improving supply chains, and raising public awareness.
The global increase in vaccine coverage also has broader societal and economic effects. Healthier populations contribute to stronger economies by reducing absenteeism and boosting productivity. Governments and organizations have recognized that investing in vaccination yields a high return in terms of lives saved and economic growth.
Experts stress that the success of vaccination programs in 2024 is the result of years of collaboration among international organizations, governments, and local health workers. Public education campaigns and community outreach played a key role in ensuring families brought their children to clinics and vaccination centers.
In addition to malaria, vaccines against diseases such as measles, polio, and diphtheria contributed to the record figures. The combined effect of these immunization programs is a significant reduction in child mortality rates worldwide. Health authorities are optimistic that the trends seen in 2024 will continue as more countries expand their vaccination programs.
Despite these successes, challenges remain. Some regions still face logistical difficulties in delivering vaccines, vaccine hesitancy, and funding gaps. Experts call for continued investment and international cooperation to ensure that life-saving vaccines reach every child, especially in low-income and conflict-affected countries.
The achievements of 2024 highlight the critical role of vaccines in improving global health. By preventing millions of deaths and providing economic benefits, vaccines demonstrate their value as one of the most effective public health interventions available today. Governments, health organizations, and communities are encouraged to build on this momentum to save even more lives in the coming years.